Problem Gambling Severity Index
Using data collected as part of the Treatment Needs and Gap Analysis programme of research, GambleAware has worked with UCL to produce maps of Great Britain which show the prevalence of problem gambling severity in each Local Authority area, as identified using the Problem Gambling Severity Index (PGSI), as well as maps showing Consumer Indicator Data including accessibility to.
- Problem Gambling Severity Index Formula
- Problem Gambling Severity Index Definition
- Problem Gambling Severity Index Calculation
- Problem Gambling Severity Index Chart
- Problem Gambling Severity Index Measures
www.gambler-addiction-index.com
- Problem Gambling Severity Index 0 Never 1 Sometimes 2 Most of the time 3 Almost always. This self-assessment is based on the Canadian Problem Gambling Index. It will help you decide if you wish to seek other forms of support or information. When you gambled, did you go back another day to.
- Problem Gambling Severity Index This self-assessment is based on the Canadian Problem Gambling Index. It will give you a good idea of whether you need to take corrective action. Thinking about the last 12.
Problem Gambling Severity Index Formula
The Gambler Addiction Index (GAI) is designed for gambler assessment, screening, or testing. The GAI has been standardized on people in treatment for gambling, probationers on gambler caseloads, and outpatient gambler groups. The GAI is an automated (computer scored), self-report assessment instrument, or test that consists of 166 items and takes 30 to 35 minutes to complete. The GAI is written at a high 5th to low 6th grade reading level. From test data (answers) input, GAI�s are computer scored with reports printed on-site, within 2 � minutes.
Problem gambling is clinically defined as an impulse control disorder (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, 4th edition). The GAI contains a reformatted DSM-IV Gambling Scale. Problem gamblers have strong impulses to gamble, despite harmful life consequences. In addition, the GAI contains a Gambling Severity Scale that measures gambling intensity. These two GAI scales codetermine a meaningful gambler profile. No other gambler test incorporates these two gambling measures, or scales.
Problem Gambling Severity Index If you think you may have a problem with gambling then you can complete this screening tool. It only takes a few minutes to complete and we don’t hold or store any of the data. Thinking about the last week (if in weekly counselling) or the last year (if in your initial assessment session). The Problem Gambling Severity Index (PGSI) is the standardised measure of at risk behaviour in problem gambling. It is a tool based on research on the common signs and consequences of problematic gambling. Assessing where your client is now can help you make informed decisions on how to assist them. Take your client through the PGSI quiz.
Another unique GAI feature is its Truthfulness Scale. Gamblers are notorious liars. When asked about their gambling, most problematic gamblers attempt to rationalize their gambling, deny extensive gambling involvement, or attempt to minimize it. In other words, when assessing gamblers, the evaluator needs to know if the client was honest and truthful. No other gambler test contains a Truthfulness Scale.


Seven GAI Measures
The Gambler Addiction Index (GAI) contains seven scales or measures: 1. Truthfulness Scale, 2. Gambling Severity Scale, 3. DSM-IV Gambling Scale, 4. Alcohol Scale, 5. Drug Scale, 6. Suicide Scale, and 7. Stress Coping Abilities (Stress Management) Scale. These GAI Scales (measures) embody areas of inquiry considered, by many, as necessary for gambler understanding.
Problem Gambling Severity Index Definition
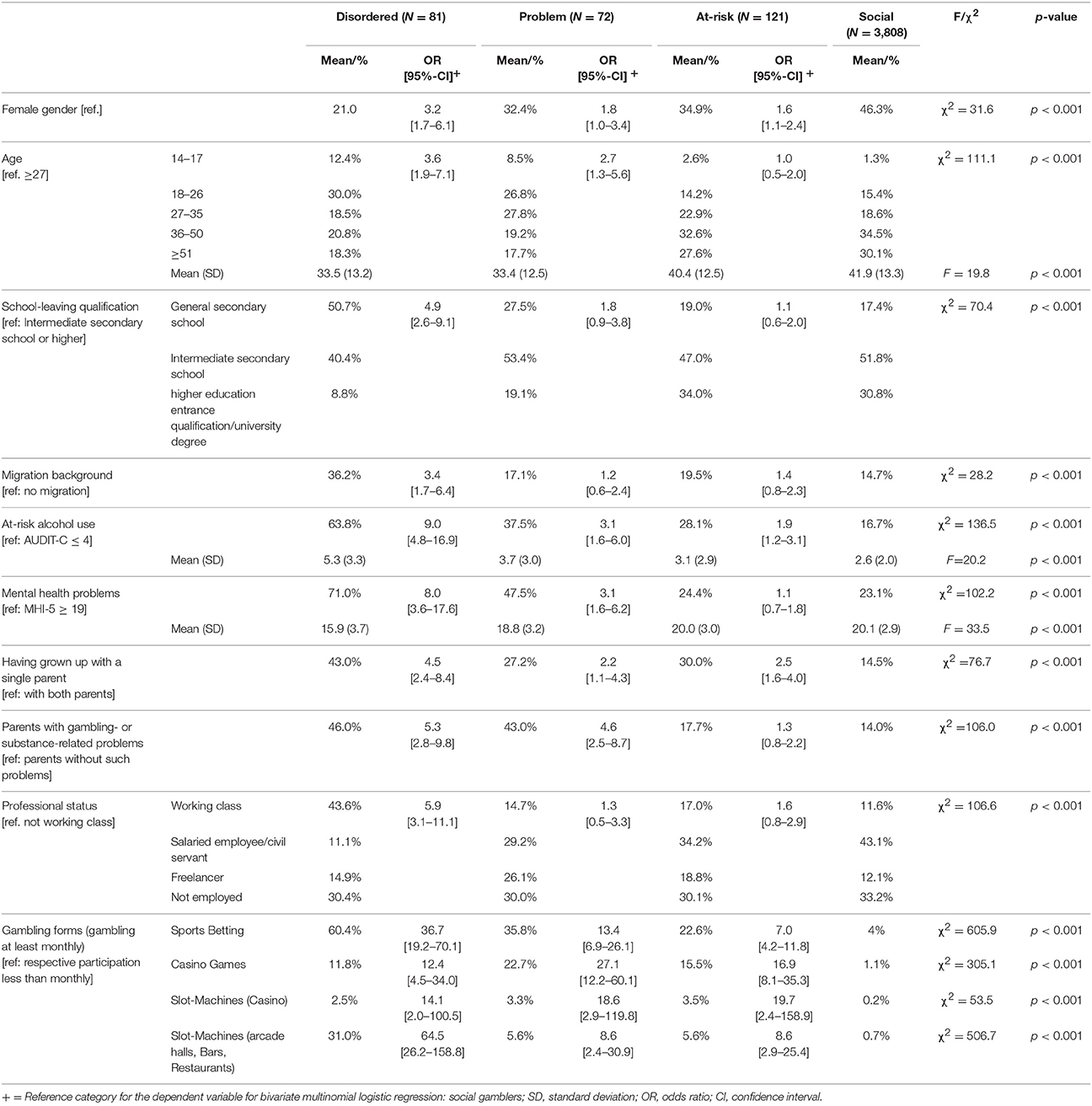
Problem Gambling Severity Index Calculation
